Familiarize Yourself with the Structure and Format of the IELTS Exam
Preparing for the IELTS exam can seem daunting, but understanding its structure and format is the first step to success. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you get acquainted with what to expect on test day.
Four sections of the IELTS
LISTENING
– You will listen to four recorded texts – two monologues and two conversations.
– You will hear the recordings once only. Different accents, including British, Australian, New Zealand, and North American, are used.
– Part 1: A conversation between two people set in an everyday social context, e.g. a conversation in an accommodation agency.
– Part 2: A monologue set in an everyday social context, e.g. a speech about local facilities.
– Part 3: A conversation between up to four people set in an educational or training context, e.g. a university tutor and a student discussing an assignment.
– Part 4: A monologue on an academic subject, e.g. a university lecture.
– There are 40 questions. A variety of different question types are used.
30 Minutes
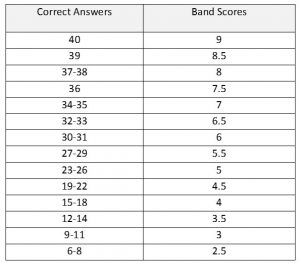
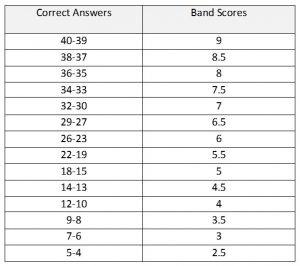
– Band 9: 39-40 correct answers out of 40
– Band 8: 35-38 correct answers
– Band 7: 30-34 correct answers
– Band 6: 23-29 correct answers
– Band 5: 16-22 correct answers
– Band 4: 10-15 correct answers
– Band 3: 6-9 correct answers
– Band 2: 4-5 correct answers
– Band 1: 1-3 correct answers
– Band 0: 0 correct answers (did not attempt the test or provided completely incorrect answers)
READING
– IELTS Academic – three sections
– For each section you will be given one long reading passage with tasks.
– All the topics are of general interest to students at undergraduate or postgraduate level.
– The texts may be written in different styles and may contain diagrams, graphs, or illustrations.
– The texts will come from a variety of sources (e.g. books, journals, newspapers).
– There are 40 questions. A variety of different question types are used.
——————-
– IELTS General Training – three sections
– You will be presented with five or six texts of varying length with tasks.
– Section 1: contains two or three short texts or several shorter texts on everyday topics.
– Section 2: contains two short, work-related, factual texts.
– Section 3: contains one longer text on a topic of general interest.
– The texts will come from a variety of sources (e.g. advertisements, company handbooks, official documents, books, newspapers).
– There are 40 questions. A variety of different question types are used.
60 Minutes
IELTS General
IELTS Academic
WRITING
– IELTS Academic Task 1:
– Describe visual information (graph, table, chart, diagram) in own words.
– Write at least 150 words.
– Time limit: about 20 minutes.
– IELTS General Training Task 1:
– Respond to a situation (e.g., writing a letter asking for information or explaining a situation).
– Write at least 150 words.
– Time limit: about 20 minutes.
– IELTS Academic and IELTS General Training Task 2:
– Discuss a point of view, argument, or problem.
– Write at least 250 words.
– Time limit: about 40 minutes.
60 Minutes
The examiner will assess your writing on the 4 marking criteria below. Each criterion is worth 25% of your total marks for writing task 1.
• Task Achievement / Response
• Coherence and Cohesion
• Lexical Resource (Vocabulary)
• Grammatical Range and Accuracy
SPEAKING
– Part 1 (4–5 minutes): The Examiner asks you general questions about yourself and a range of familiar topics, such as home, family, work, studies, and interests.- Part 2 (3–4 minutes): You will be given a card which asks you to talk about a topic.
– You will have 1 minute to prepare before speaking for up to 2 minutes. The Examiner may then ask one or two questions on the same topic.
– Part 3 (4–5 minutes): The Examiner asks more questions that are connected to the topic of Part 2. These questions give you an opportunity to discuss more abstract issues and ideas.
11-14 Minutes
Here are the four key criteria used by examiners to assess the speaking performance:
– Fluency & Coherence (FC): This assesses the ease and flow of your speech, your ability to express yourself clearly and connect your ideas effectively.
– Lexical Resource (LR): This assesses the range of vocabulary you use, including your use of idioms and synonyms, and your ability to express yourself precisely.
– Grammatical Range and Accuracy (GRA): This assesses the variety and correctness of grammatical structures you use in your speech.
– Pronunciation (P): This assesses your ability to be understood clearly, including your pronunciation of individual sounds, word stress, and intonation.
